

In simple interest problems, a single investment is made and the interest is paid to the lender as one lump sum at the end of the term. The present value represents the amount invested at the beginning of the term. The interest is the present value times the nominal annual rate times the number of years in the term. The future value is the present value plus the interest. The simple interest formulas are summarized in the following table.
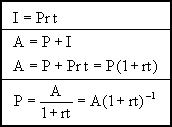
where
Simple interest is not commonly used and is presented here only to review the fundamental concepts.
Given an investment of $3,000 at 5% simple interest for 6 years, find the interest earned and the future value.
P = 3,000
r = 0.05
t = 6
A = ?
I = ?
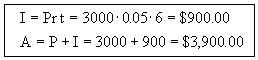
Find the present value of an investment if the future value is $1,000. The investment pays 4.5% simple interest for seven years.
The present value is the amount that must be invested in order to get the indicated future value.
P = ?
r = 0.045
t = 7
A = 1,000
I
![]()
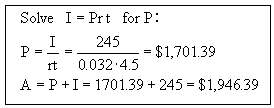
The interest on a 4.5 year investment paying 3.2% simple interest was $245. How much was invested and what was the future value?
P = ?
r = 0.032
t = 4.5
A = ?
I = 245
What is the future value of an investment of $600 at 2.3% simple interest for 10 years?
P = 600
r = 0.023
t = 10
A = ?
I
![]()