The standard deviation is a measure of dispersion. A small value indicates that the data is tightly grouped about the mean. A high value indicates that the data is spread widely on either side of the mean. The examples below illustrate this property.
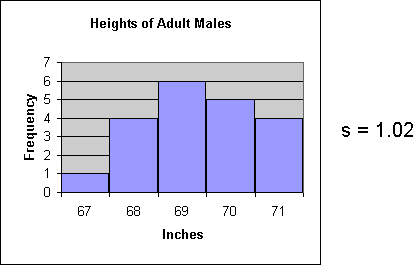
The first example represents a sample of adult males whose heights are tightly grouped about the mean. The standard deviation is 1.02 which is the lowest value among the three examples on this page.
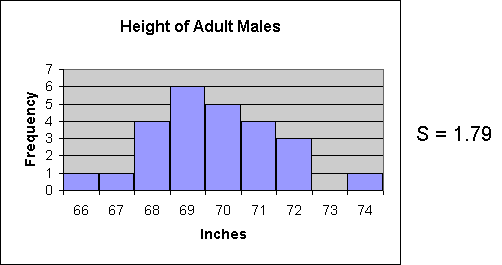
The second example is the one used on the page that led to this one. The standard deviation is 1.79.
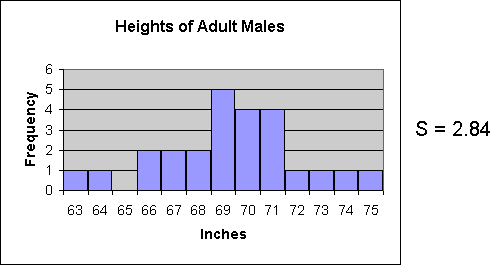
The final example represents a data set in which the data is very spread out. The corresponding standard deviation is the largest of these three examples at 2.84.